Standard Glass Thickness for Cabinet Doors
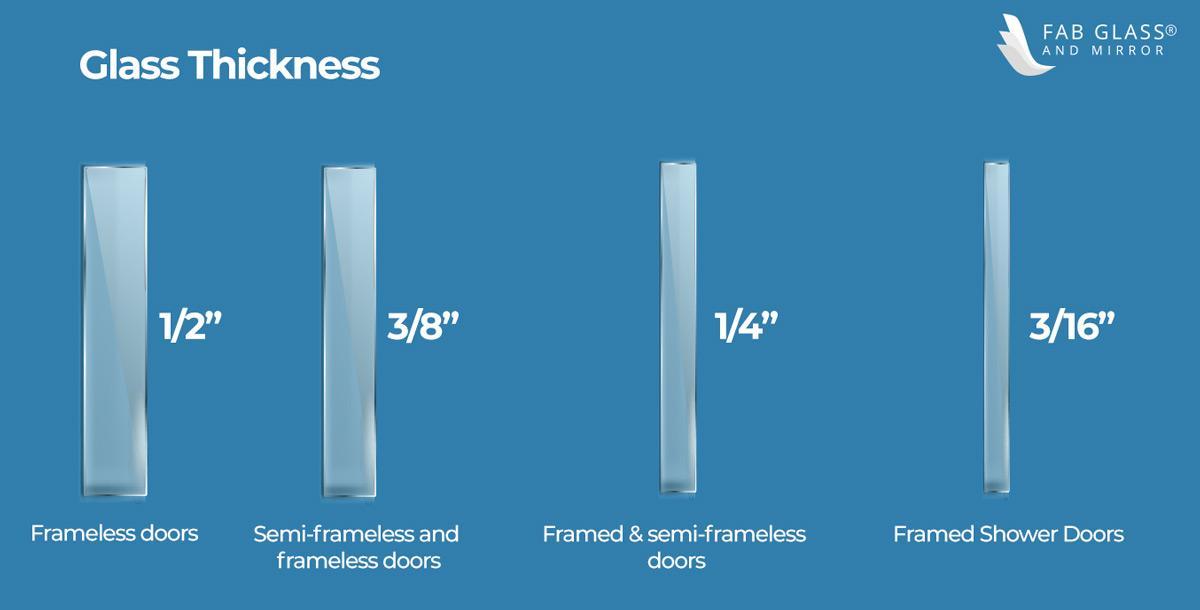
Glass cabinet doors are a popular choice for homeowners who want to add a touch of elegance and sophistication to their kitchens and bathrooms. They offer a variety of advantages, including increased light transmission, a modern aesthetic, and easy cleaning. When selecting glass cabinet doors, one crucial factor to consider is the thickness of the glass. Choosing the right glass thickness ensures durability, safety, and a visually appealing finish.
Factors Influencing Glass Thickness Selection
The choice of glass thickness for cabinet doors is influenced by several factors, including the style of the cabinets, the weight of the doors, and the intended use.
- Style: The style of the cabinets can influence the glass thickness. For example, contemporary cabinets often feature thinner glass to create a minimalist look, while traditional cabinets may use thicker glass for a more substantial appearance.
- Weight: The weight of the cabinet doors is another important factor. Heavier doors require thicker glass to provide adequate support and prevent sagging.
- Intended Use: The intended use of the cabinets also plays a role. Cabinets used in high-traffic areas or those containing heavy items may benefit from thicker glass for added durability.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Different Glass Thicknesses
- Thin Glass (1/8″ – 1/4″):
- Advantages: Lightweight, affordable, and allows for a more modern and minimalist aesthetic.
- Disadvantages: Less durable, susceptible to breakage, and may not be suitable for heavy doors or high-traffic areas.
- Medium Glass (3/16″ – 1/2″):
- Advantages: Provides a good balance of strength and affordability, suitable for most standard cabinet doors.
- Disadvantages: May be heavier than thinner glass, requiring stronger hinges and framing.
- Thick Glass (5/8″ – 1″):
- Advantages: Extremely durable, suitable for heavy doors and high-traffic areas, and can withstand significant impact.
- Disadvantages: Heavy, expensive, and may require specialized framing and hardware.
Common Glass Thicknesses for Cabinet Doors

Standard glass thickness for cabinet doors – The thickness of glass used for cabinet doors significantly impacts their visual appeal, durability, and overall functionality. While thinner glass may appear more delicate and offer a less obstructed view, thicker glass provides greater strength and resistance to breakage. Understanding the common glass thicknesses used for cabinet doors allows you to choose the option that best suits your needs and design preferences.
Common Glass Thicknesses and Applications
Here’s a comprehensive list of the most common glass thicknesses used for cabinet doors, along with their typical applications and advantages and disadvantages:
| Glass Thickness (mm) | Glass Thickness (inches) | Typical Applications | Advantages/Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| 3 mm | 0.12 inches | Small cabinet doors, decorative elements, shelves, and light-duty applications. |
|
| 4 mm | 0.16 inches | Medium-sized cabinet doors, display cases, and applications where some strength is required. |
|
| 5 mm | 0.20 inches | Standard cabinet doors, larger display cases, and applications requiring moderate strength. |
|
| 6 mm | 0.24 inches | Large cabinet doors, heavy-duty applications, and areas with high traffic. |
|
| 8 mm | 0.31 inches | High-end cabinets, commercial applications, and areas with extreme impact risks. |
|
Illustrative Image of Cabinet Doors with Different Glass Thicknesses
Imagine a cabinet door with a simple, rectangular frame. The door is divided into three sections, each showcasing a different glass thickness. The leftmost section features 3 mm glass, appearing almost transparent and offering a clear view of the contents within. The middle section showcases 6 mm glass, presenting a slightly more opaque appearance while still maintaining a good level of clarity. The rightmost section displays 8 mm glass, exhibiting a noticeably thicker and more robust look, potentially obscuring the view slightly due to its increased thickness.
Glass Types for Cabinet Doors: Standard Glass Thickness For Cabinet Doors
Cabinet doors made of glass offer a unique aesthetic appeal and can enhance the overall look of your kitchen or bathroom. However, the type of glass you choose will significantly impact the durability, transparency, and safety of your cabinet doors.
Tempered Glass, Standard glass thickness for cabinet doors
Tempered glass is a type of safety glass that is strengthened by a process of heating and rapid cooling. This process creates internal stresses within the glass, making it significantly stronger than standard glass. Tempered glass is highly resistant to shattering and will break into small, blunt pieces rather than sharp shards, making it a safe choice for cabinet doors. It’s also resistant to scratches and abrasions, making it a good option for high-traffic areas.
Laminated Glass
Laminated glass is constructed by bonding two or more layers of glass together with a layer of polyvinyl butyral (PVB) film sandwiched between them. The PVB film holds the glass fragments together in case of breakage, preventing sharp shards from flying. Laminated glass is also known for its sound-dampening properties and its ability to block ultraviolet (UV) rays, making it a good choice for cabinets in sun-exposed areas.
Frosted Glass
Frosted glass is a type of glass that has been treated to create a translucent, opaque finish. The frosting process can be achieved by etching, sandblasting, or acid-etching the glass surface. Frosted glass provides privacy while still allowing some light to pass through. It is commonly used for cabinet doors in bathrooms and bedrooms where privacy is desired.
You know, standard glass thickness for cabinet doors is pretty basic stuff. But then you have those fancy wooden gun cabinets with glass doors, like the ones you can find at this website. Those things need thicker glass, right?
You wouldn’t want your prized collection to be vulnerable to a stray elbow. So, yeah, standard glass thickness is important, especially when you’re dealing with valuable stuff.
You know, when it comes to cabinet doors, standard glass thickness is usually around 3mm. But for a real statement piece, check out those metal and glass curio cabinets. They’re like a whole other level of glass thickness, adding a touch of luxury and a whole lot of “wow” factor.
So, yeah, standard glass is fine, but if you’re going for that extra oomph, you might want to think about something a little thicker.
